A number of metabolic conditions involve the liver and can cause chronic liver disease, leading to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Metabolic Liver Disease develops when the liver could no longer function properly. The most familiar metabolic liver diseases are Wilson’s Disease, AATD and Hereditary Hemochromatosis. These diseases can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated properly on time.
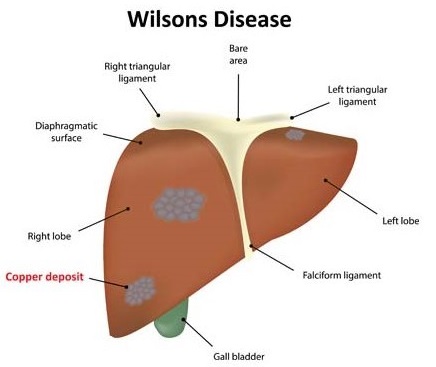
Wilson’s Disease:
A rare genetic health problem which is caused by the accumulation of copper in organs like liver and lead to cirrhosis or acute liver failure. Doctor will work closely with a nutritionist to help reduce dietary intake of copper. This may include avoiding foods such as shellfish mushrooms nuts and chocolate. Other treatment may include medications to enhance the excretion of copper from the body. A liver transplant may be necessary in patients with acute liver failure or when cirrhosis leads to liver failure.
AATD (Alpha-I Antitrypsin Deficiency):
The body produces an excessive amount of irregular protein that gets accumulated in the liver. This can slowly lead to scarring, liver cancer, adult-onset chronic hepatitis, liver damage, and cirrhosis. There is no cure for AATD. Treatment focuses on reducing the complications of the associated chronic liver disease. Patients with AATD are advised not to smoke tobacco or drink alcohol. For adults with end-stage liver disease due to AATD, liver transplantation is sometimes an option.
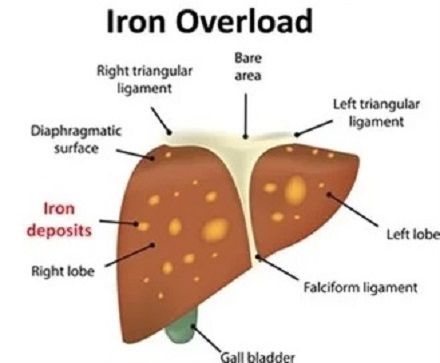
Hereditary Hemochromatosis:
It is a genetic abnormality and generally called as iron overload disease. The body absorbs and stores iron more than the permissible limits for the human body. This excess iron is stored in organs like pancreas and liver and can lead to liver cirrhosis. Hereditary Hemochromatosis can be easily diagnosed with a blood test. Therapeutic Phlebotomy is a treatment procedure used to treat the Hereditary Hemochromatosis by removing excess iron from the body.
